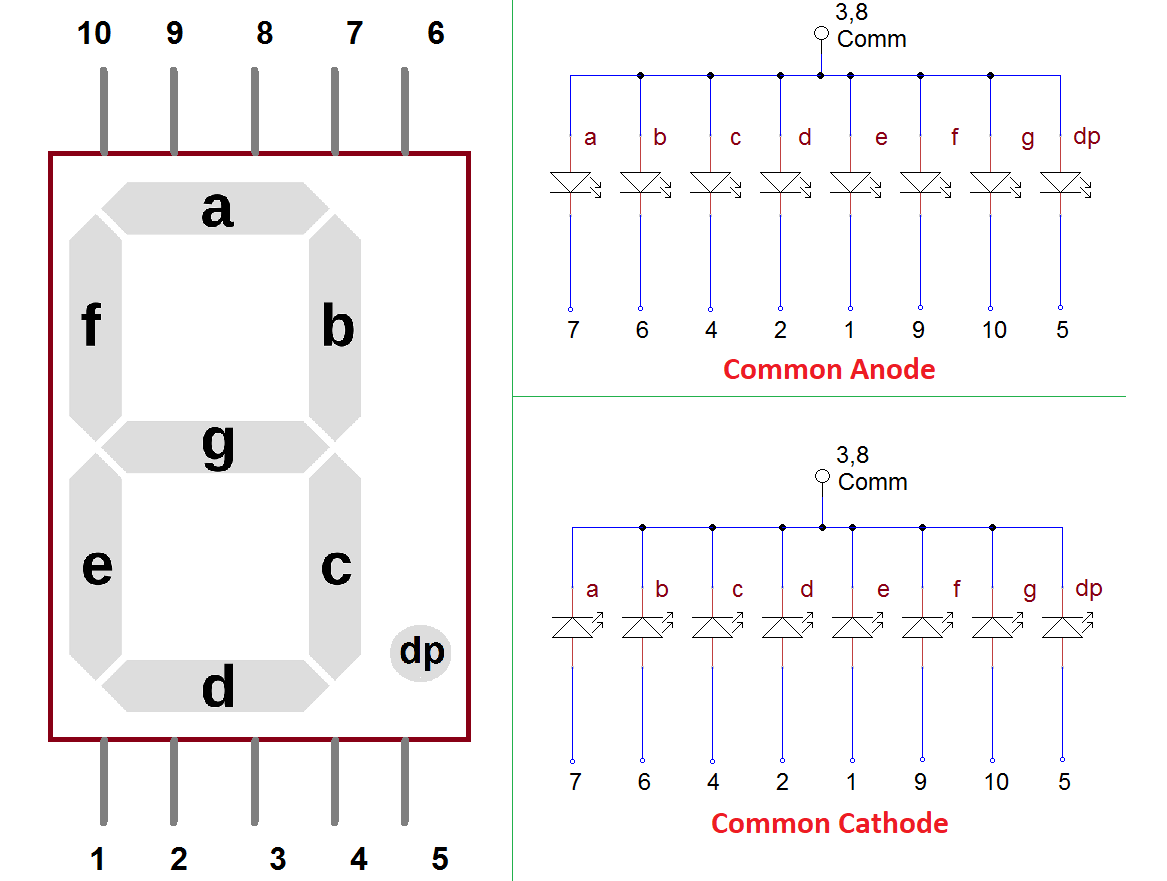
Seven segment display:
Raspberry Pi:
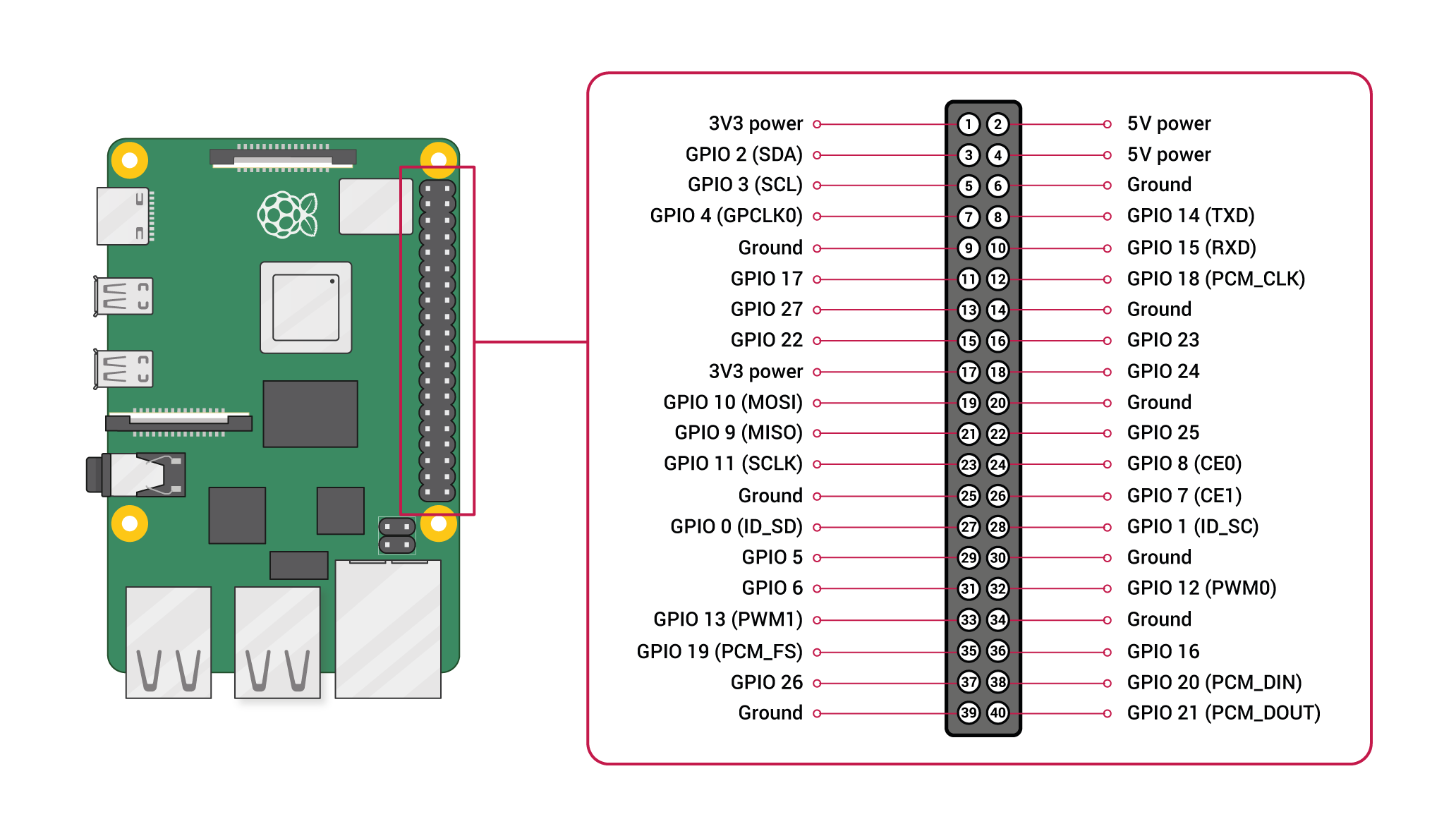
Pin configuration:
1. Vin: Two 5v pins and two 3v3 pins used for providing power supply, where processor works on 3.3v.
Seven segment pins connections with Raspberry pi:
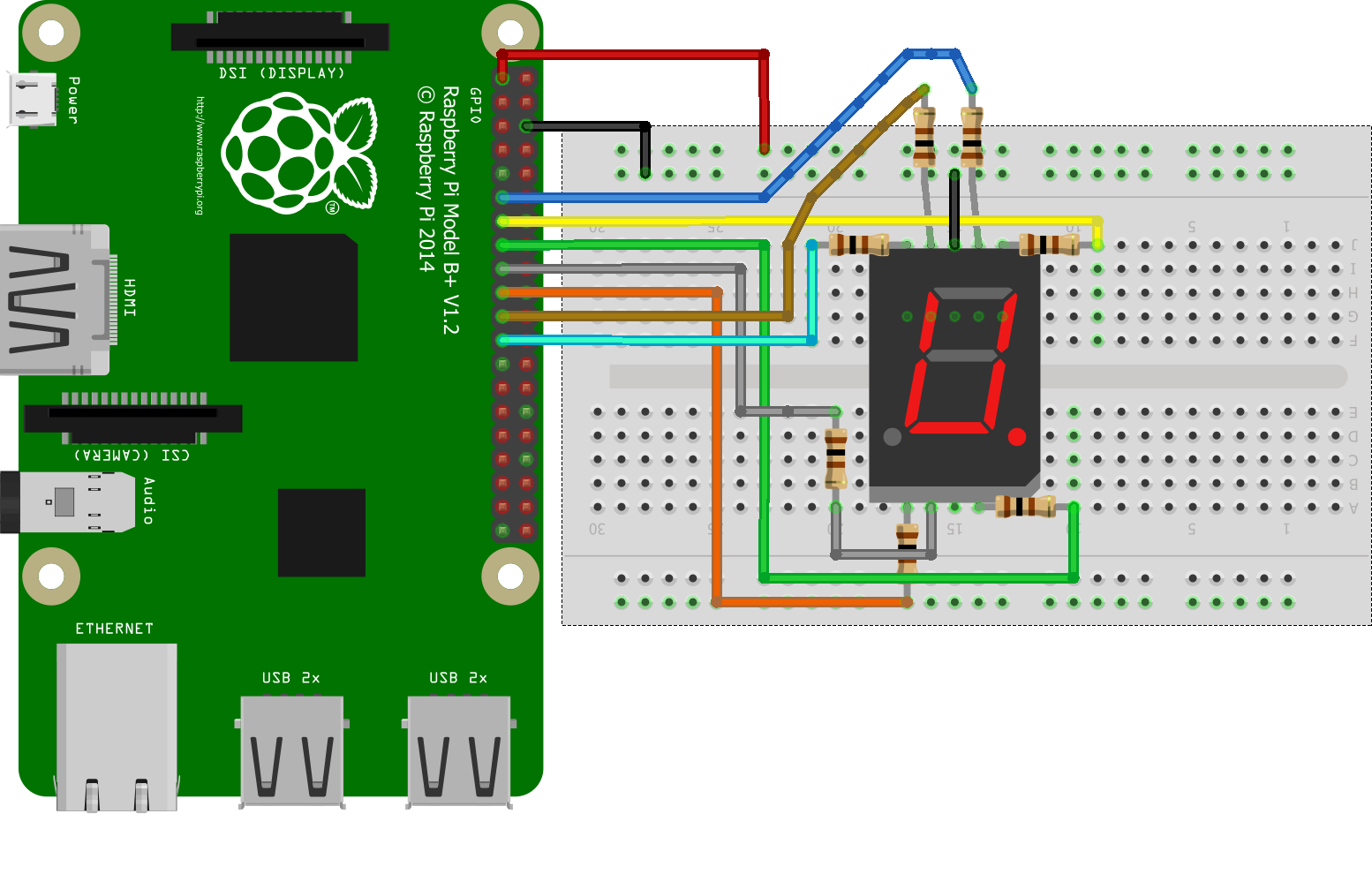
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO import time DISPLAY=[0x3F,0x06,0x5B,0x4F,0x66,0x6D,0x7D,0x07,0x7F,0x67] GPIO.setwarnings(False) GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) GPIO.setup(13,GPIO.OUT) GPIO.setup(6,GPIO.OUT) GPIO.setup(16,GPIO.OUT) GPIO.setup(20,GPIO.OUT) GPIO.setup(21,GPIO.OUT) GPIO.setup(19,GPIO.OUT) GPIO.setup(26,GPIO.OUT) GPIO.setup(12,GPIO.OUT) Def PORT(pin) if(pin&0x01==0x01): GPIO.output(13,1) else: GPIO.output(13,0) if(pin&0x02==0x02): GPIO.output(6,1) else: GPIO.output(6,0) if(pin&0x04==0x04): GPIO.output(16,1) else: GPIO.output(16,0) if(pin&0x08==0x08): GPIO.output(20,1) else: GPIO.output(20,0) if(pin&0x10==0x10): GPIO.output(21,1) else: GPIO.output(21,0) if(pin&0x20==0x20): GPIO.output(19,1) else: GPIO.output(19,0) if(pin&0x40==0x40): GPIO.output(26,1) else: GPIO.output(26,0) if(pin&0x80==0x80): GPIO.output(12,1) else: GPIO.output(12,0) While 1: For x in range(10): Pin=DISPLAY[x] PORT(pin) time.sleep(1)